“yum history” feature of yum is a mostly overlooked but very powerful utility in Linux. It can be used to rollback/redo/undo yum transaction to a state where everything was working fine.
yum history
“yum history list” command when run without any arguments produces output similar to shown below. “yum history” or “yum history list” by default shows last 20 yum transactions.
# yum history list
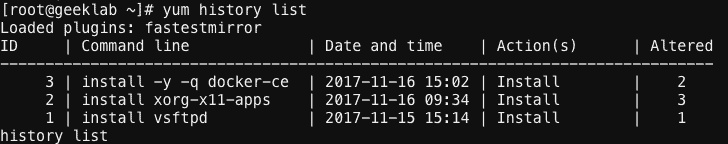
Here,
ID: Uniquely identifies a yum transaction.
Command line:
Date and time: Date and time of transaction.
Action(s): Action performed in the transaction like Install, update etc. Detail list is given below.
| Action | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Downgrade | D | At least one package has been downgraded to an older version. |
| Erase | E | At least one package has been removed. |
| Install | I | At least one new package has been installed. |
| Obsoleting | O | At least one package has been marked as obsolete. |
| Reinstall | R | At least one package has been reinstalled. |
| Update | U | At least one package has been updated to a newer version. |
Altered: Number of packages that were affected by a transaction and additional information like whether rpmdb database was changed before are after transaction etc. Detail list is given below.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| < | Before the transaction finished, the rpmdb database was changed outside Yum. |
| > | After the transaction finished, the rpmdb database was changed outside Yum. |
| * | The transaction failed to finish. |
| # | The transaction finished successfully, but yum returned a non-zero exit code. |
| E | The transaction finished successfully, but an error or a warning was displayed. |
| P | The transaction finished successfully, but problems already existed in the rpmdb database. |
| s | The transaction finished successfully, but the –skip-broken command-line option was used and certain packages were skipped. |
To display all transactions, use the all option.
# yum history list all
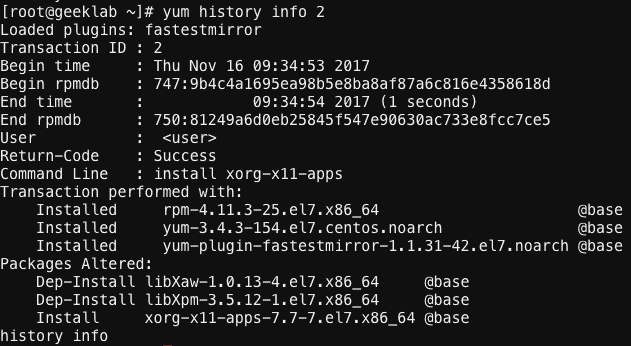
Information on a specific transaction
If you know the transaction ID of a yum transaction, you can get a detailed view on it using the below command.
# yum history info 1
For example :
you can also use the package name with yum history command. For Example :
# yum history info vsftpd
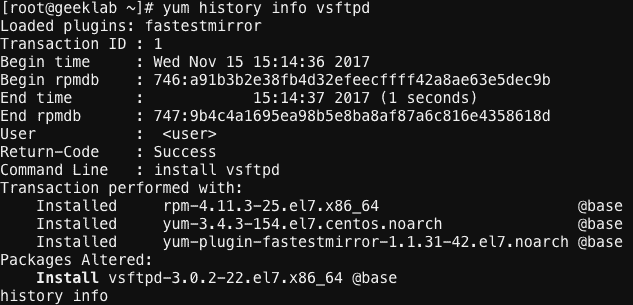
The above command will show all the transaction like install, update, removal of the package vsftpd.
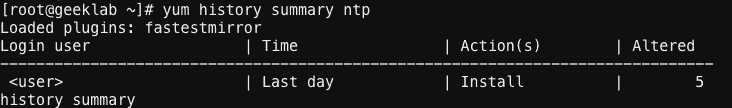
You can also get a summary of transaction history on a specific package using the the summary option. For Example :
Rollback or redo a yum transaction
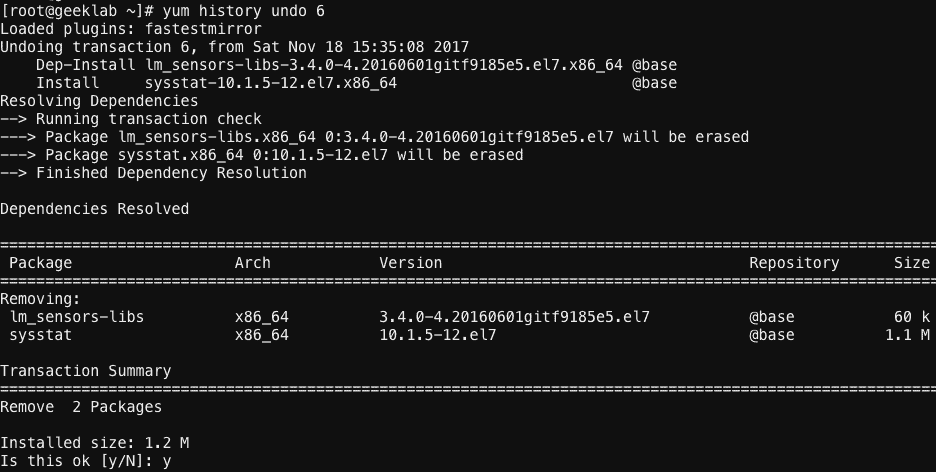
You can undo a specific yum transaction using the command below syntax:
# yum history rollback [transaction_ID]
For example:
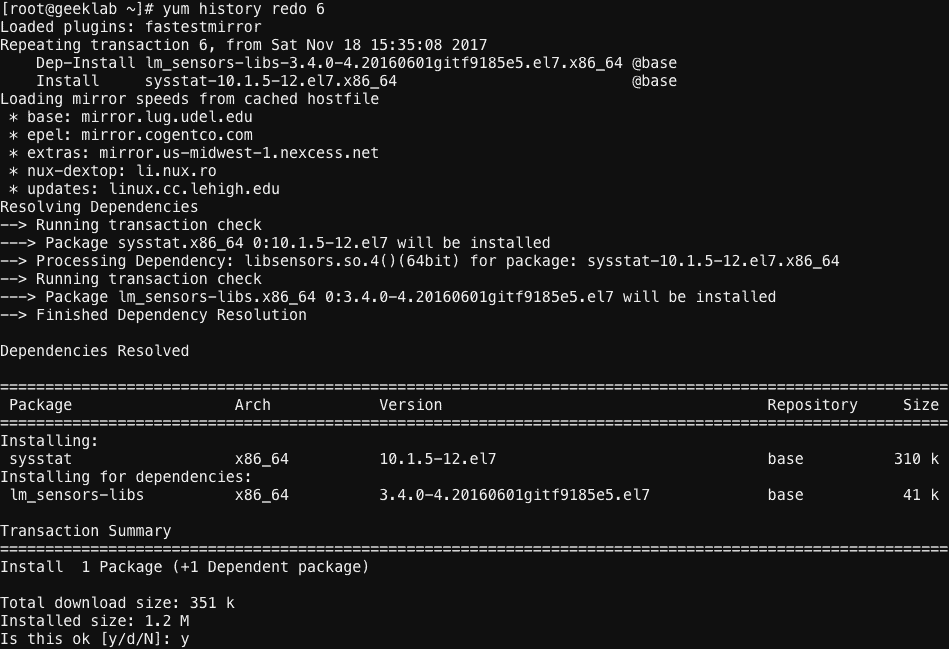
Similarly you can also redo the yum transaction. For Example :
# yum history redo [transaction ID]
We will redo the removed sysstat package removal using the command shown in the figure below.
The redo sub-command can also take some optional arguments before we specify a transaction:
force-reinstall – reinstalls any packages that were installed in that transaction (via yum install, upgrade or downgrade).
force-remove – removes any packages that were updated or downgraded.
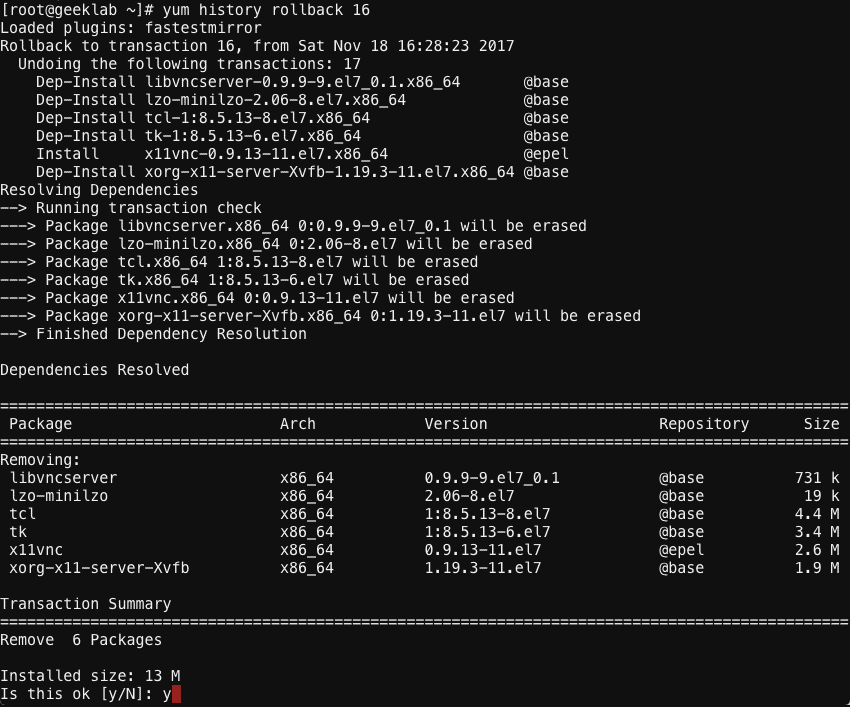
Rollback yum transaction to a certain point
With yum history command you can roll back all transaction until a particular transaction ID. For example, if you specify transaction ID of 16, all transactions from the latest to transaction ID 16 will be rolled back. For Example :
# yum history rollback 16