SELinux can either be in an enabled or a disabled state. In order to check in which state it is running, we can make use of the getenforce command. There are two modes in which SELinux runs:
There are two modes in which SELinux runs:
- Enforcing: This is the enabled state where all rules are applied.
- Permissive: In this state, SELinux will not deny any access; however, denials are logged.
sestatus is used to get the status of a system running SELinux. It displays data about whether SELinux is enabled, disabled, the loaded policy and whether it is in enforcing or permissive mode. It can also be used to display the security context of files and processes listed in the /etc/sestatus.conf file.
To show the state of SELinux, you can use the sestatus command:
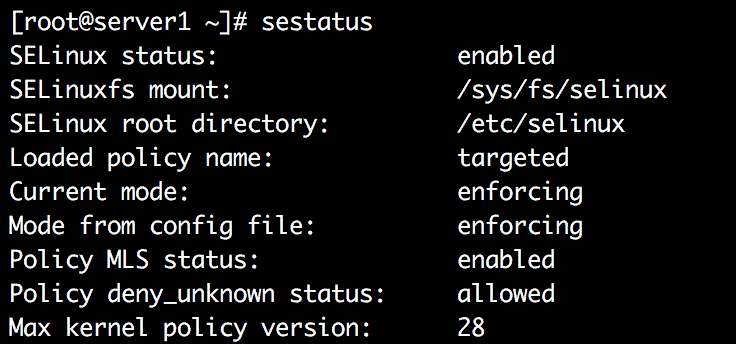
If you encounter below error, while running the sestatus command:
sestatus: command not found
you may try installing the below package as per your choice of distribution.
| Distribution | Command |
|---|---|
| Debian | apt-get install policycoreutils |
| Ubuntu | apt-get install policycoreutils |
| Kali Linux | apt-get install policycoreutils |
| CentOS | yum install policycoreutils |
| Fedora | dnf install policycoreutils |
| Raspbian | apt-get install policycoreutils |
sestatus Command Examples
1. To see the SELinux status:
# sestatus
2. To see the current status of the booleans:
# sestatus -b
3. To check the contexts of files and processes listed in /etc/sestatus.conf file:
# sestatus -v
4. To see the sestatus help:
# sestatus --help
Conclusion
There are three different modes when it comes to SELinux. While Enhanced is the only true mode that really protects us and enhances our server’s security, there are two other modes: Disabled and Permissive. Disabled means SELinux is turned off.