The lsblk command displays information about all block storage devices that are currently available on the system. The output is displayed in a tree-like format with each physical device at the top of the tree and each partition or logical volume branching off from that device. The information displayed includes names, major and minor numbers, size, device type, and mount point.
Syntax
The syntax of the lsblk command is:
# lsblk [options] [device name] lsblk COMMAND OPTIONS
The following table lists some of the options available with the lsblk command.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -a | List empty devices as well. |
| -e {device list} | Exclude devices from output that you provide as a list of comma-separated major device numbers. |
| -f | Output additional file system information. |
| -l | Output results in list format. |
| -m | Output permissions information for devices. |
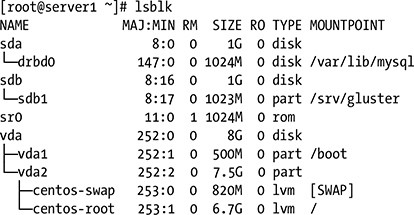
Here is an example of lsblk command output without any arguments passed to it.
If you encounter below error while running the lsblk command:
lsblk: command not found
you may try installing below package as per your choice of distribution:
| Distribution | Command |
|---|---|
| OS X | brew install util-linux |
| Debian | apt-get install fdisk |
| Ubuntu | apt-get install fdisk |
| Alpine | apk add util-linux |
| Arch Linux | pacman -S util-linux |
| Kali Linux | apt-get install fdisk |
| CentOS | yum install util-linux |
| Fedora | dnf install util-linux |
| Raspbian | apt-get install util-linux |
lsblk Command Examples
1. List all storage devices in a tree-like format:
# lsblk
2. Also list empty devices:
# lsblk -a
3. Print the SIZE column in bytes rather than in a human-readable format:
# lsblk -b
4. Output info about filesystems:
$ lsblk -f
5. Use ASCII characters for tree formatting:
# lsblk -i
6. Output info about block-device topology:
# lsblk -t
7. Exclude the devices specified by the comma-separated list of major device numbers:
# lsblk -e 1,7
8. Display a customized summary using a comma-separated list of columns:
# lsblk --output NAME,SERIAL,MODEL,TRAN,TYPE,SIZE,FSTYPE,MOUNTPOINT