To set up a domain name, there are a couple of steps to do. First, you need to purchase a domain name from a domain name registrar. Second, you need to set up DNS records for your domain by using a DNS hosting service.
Let’s do this one by one.
Prerequisite – A domain name from a domain registrar
I assume we have already purchased a domain name from any registrar such as GoDaddy, GoogleDomains, Bluehost or BigRock to name a few. Learn more about domain name registrars.
Set up DNS records for your domain
Let’s say you have purchased a domain called www.abcde.com from GoDaddy. I am using GoDaddy as the domain name provider and using its DNS hosting service. The admin interface of all the domain name providers might be different once you log in, but the steps will be similar.
1. log in to Godaddy, and move on to the My Products section.
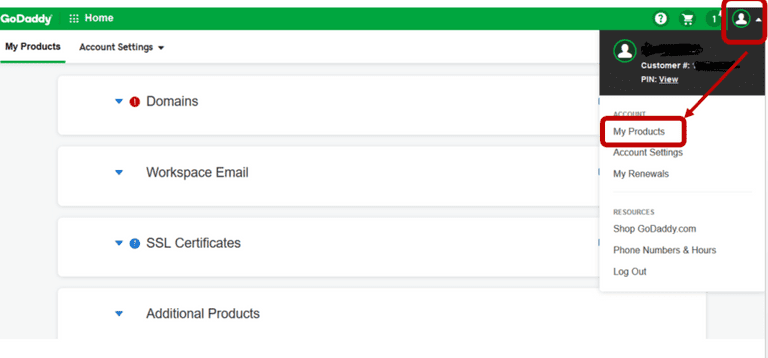
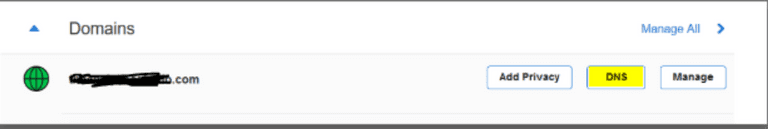
2. Click on DNS tab present at the extreme right of your domain.
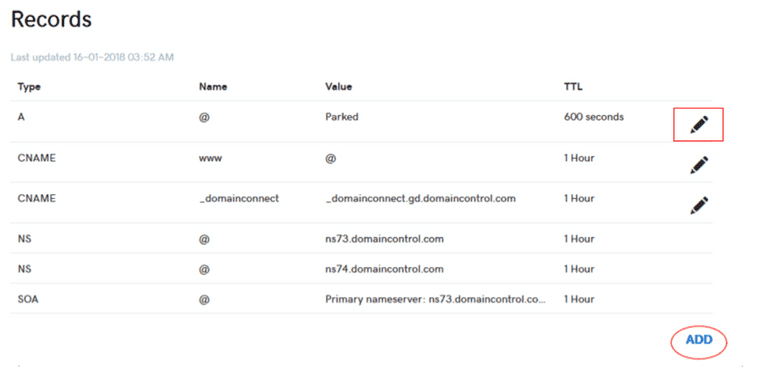
3. Once a new page Record opens, click on the edit icon (pencil icon) at the right of the Type A record.
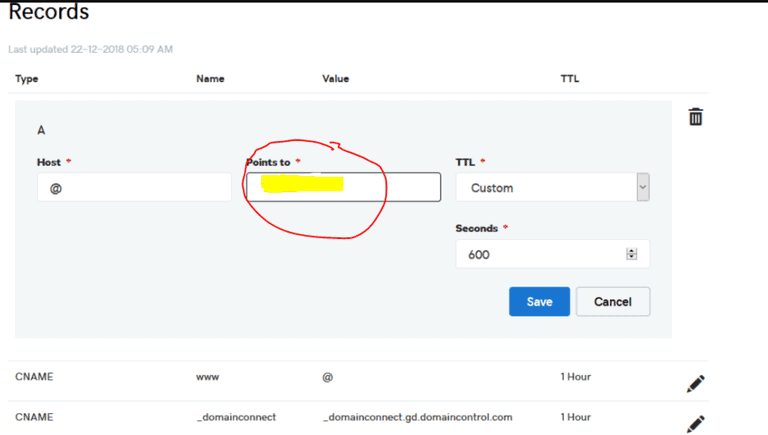
4. Put your static ip ( say a dummy ip 21.111.221.123 ) without https or http or slash in the “Points to” section (highlighted in yellow in the image below), and Save it.
That’s it. If you want to learn more about DNS, head over to this DigitalOcean article.