The getfacl command is used to retrieve the ACLs of files and directories.
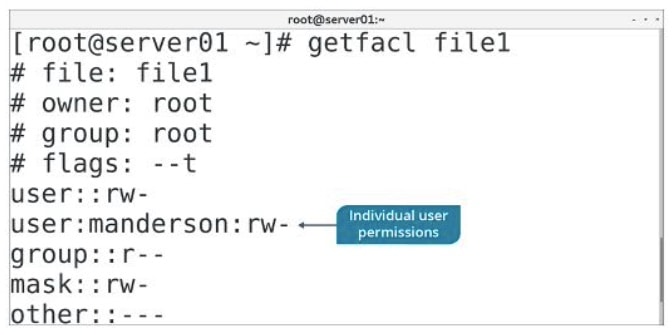
The basic output format of the getfacl command shows metadata about the object including its owner, its group, any SUID/SGID/sticky bit flags set, the standard permissions associated with the object, and the individual permission entries for users and groups.
An ACL that sets permissions for a specific user.
getfacl Command Examples
1. To get the ACL’s of a file:
# getfacl /tmp/file.txt
2. To display the file access control list:
# getfacl -a /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --access /tmp/file.txt
3. To display the default access control list:
# getfacl -d /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --default /tmp/file.txt
4. To avoid displaying comment header:
# getfacl -c /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --omit-header /tmp/file.txt
5. To Print all effective rights comments:
# getfacl -e /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --all-effective /tmp/file.txt
6. To avoid printing effective rights:
# getfacl -E /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --no-effective /tmp/file.txt
7. To skip files that only have the base ACL entries:
# getfacl -s /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --skip-base /tmp/file.txt
8. To list the ACL’s recursively:
# getfacl -R /tmp # getfacl --recursive /tmp
9. To follow the symbolic links:
# getfacl -L /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --logical /tmp/file.txt
10. To avoid following the symbolic links:
# getfacl -P /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --physical /tmp/file.txt
11. To get the tabular output format:
# getfacl -t /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --tabular /tmp/file.txt
12. Do not strip leading slash characters:
# getfacl -p /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --absolute-names /tmp/file.txt
13. To list the numeric user and group IDs:
# getfacl -n /tmp/file.txt # getfacl --numeric /tmp/file.txt
14. To get the version of the getfacl:
# getfacl -v # getfacl -version
15. To get the help for getfacl:
# getfacl -h # getfacl --help